
Subscribe to our Blog
We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.

Real PradJune 14, 202411 min read

Generating table of contents...
Optimizing JavaScript is essential for creating faster and more efficient web applications. As JavaScript becomes a critical part of web development, understanding how to optimize it can significantly improve the performance of your applications.

JavaScript can significantly impact the performance of your web application. Poorly optimized JavaScript can slow down load times, increase rendering times, and consume more CPU and battery resources. By optimizing your JavaScript, you ensure that your web application runs smoothly, providing a better user experience and potentially increasing user engagement.
Minification and compression are crucial techniques for optimizing JavaScript to enhance web application performance. These methods reduce file sizes, leading to faster load times and a better user experience.
Minification involves removing unnecessary characters from the code, such as whitespaces, comments, and unused code, without changing its functionality. This makes the files smaller and quicker to download. Popular tools for minification include:
Compression further reduces file sizes by using algorithms like Gzip or Brotli. These methods are typically applied at the server level, compressing the files before they are sent to the browser. Gzip is widely supported and easy to implement, while Brotli often offers better compression ratios.
Here's how to implement these techniques:
Code splitting is a crucial technique in JavaScript optimization. It is designed to improve performance by breaking down a large bundle of JavaScript into smaller, manageable chunks. This approach allows you to load only the necessary parts of your code at runtime, reducing the initial load time and enhancing overall performance.
Why Code Splitting is Important
Implementing Code Splitting
There are several methods to implement code splitting, depending on your setup and requirements. Here are two commonly used techniques:


Using dynamic imports, you can ensure that only the code required for the current view is loaded, reducing the initial load time and improving performance.
Lazy loading is an effective technique to enhance web performance by deferring the loading of non-essential resources.
How It Works
Lazy loading delays the loading of resources, such as images, videos, and iframes, until they are about to enter the viewport. For instance, when a user scrolls down a page, images outside the initial view are loaded only when they are about to become visible. This reduces the amount of data loaded during the initial page load.
Implementation
Loading Attribute: The simplest way to implement lazy loading is by using the loading attribute in HTML. Adding loading= "lazy" to an <img> or <iframe> tag tells the browser to defer loading until the element is near the viewport.

Intersection Observer API:
For more control, the Intersection Observer API can be used. This API allows you to observe changes in the visibility of a target element relative to its parent or the viewport. A callback function is triggered to load the resource when the element becomes visible.
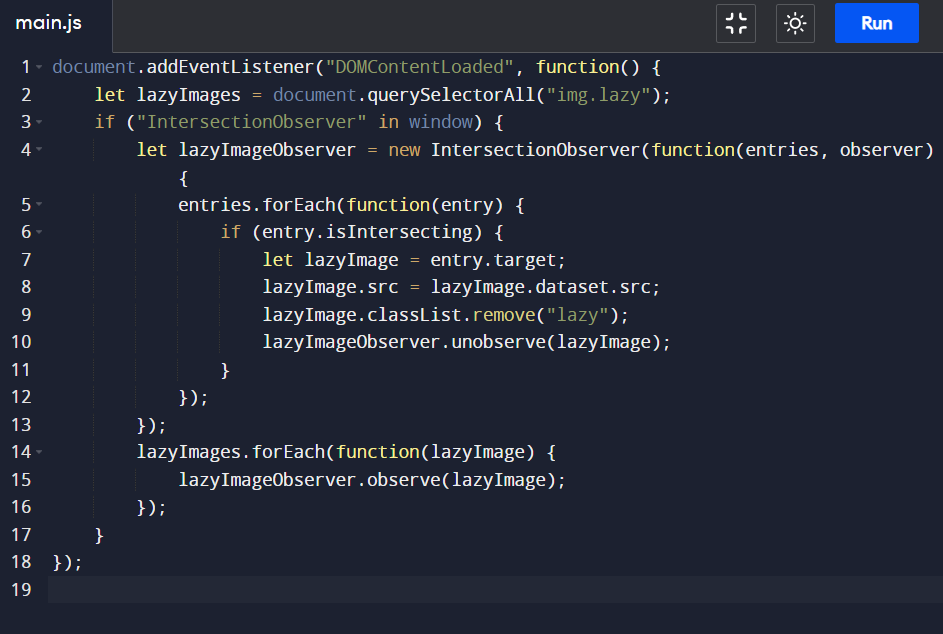
Libraries:
Several libraries, such as Lozad.js and Yall.js, can simplify the implementation of lazy loading by providing built-in functionalities to handle various media types and browser compatibility.
Benefits
Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Only the resources needed by the user are loaded, which can be particularly beneficial for users on slower internet connections.
Improved Performance: Decreasing the number of concurrent requests during the initial load can lead to smoother performance and less strain on the server.
Blocking scripts can significantly slow down your web application. When the browser encounters a script tag, it stops rendering the page until the script is fully loaded and executed. This delay impacts the overall user experience.
Strategies to Avoid Blocking Scripts
Defer and Async Attributes:
Use the defer attribute for scripts that need to be executed in the order they appear. This ensures the scripts run after the HTML has been parsed.
Use the async attribute for scripts that can be executed independently of other scripts. This allows the script to be fetched and executed asynchronously, reducing page load time.
Load Scripts at the Bottom:
Place script tags at the end of your HTML document. This ensures the browser loads and renders all HTML content before executing any JavaScript, improving perceived performance.
Inline Critical Scripts:
Inline small, critical scripts directly within your HTML. This reduces the number of HTTP requests and ensures essential scripts are available immediately.
Code Splitting:
Break down your JavaScript into smaller chunks. Load only the necessary scripts initially and defer the rest until they are needed. This reduces the initial load time and improves performance.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
Host your scripts on a CDN to take advantage of faster load times and distributed networks. CDNs can serve cached versions of your scripts from servers closer to your users.
Implementing effective caching strategies can significantly enhance the performance of web applications.
Here are some key strategies to consider:
Client-Side Caching
Server-Side Caching
Advanced Strategies
Best Practices
Reducing DOM manipulations is crucial for optimizing the performance of web applications. Here are some best practices to minimize the impact of DOM manipulations on your application's performance:
Batch Updates
Instead of updating the DOM with every change, batch multiple updates together. This can be achieved using document.createDocumentFragment(). You reduce the number of reflows and repaints by appending elements to the fragment first and then adding the fragment to the DOM. For example:

Use Event Delegation
Event delegation allows you to handle events at a higher level in the DOM rather than at the individual element level. This reduces the number of event listeners and improves performance. For instance, instead of attaching click events to multiple buttons, attach a single event listener to their parent:

Minimize Layout Thrashing
Layout thrashing occurs when you read from and write to the DOM repeatedly, causing multiple reflows and repaints. To avoid this, separate read and write operations. For example, gather all measurements first, then make the updates:

Use Efficient Methods for DOM Manipulation
Methods like innerHTML can be slower than creating elements directly and appending them. Use methods like createElement and appendChild whenever possible to build your DOM elements more efficiently.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the performance costs associated with DOM manipulations, ensuring a smoother and faster user experience for your web applications.
Efficient loops and conditionals are crucial for enhancing the performance of JavaScript applications. Here are some best practices to follow:
Choose the Right Loop:
Use for loops for known iteration counts. For iterating over arrays, prefer array methods like forEach, map, or filter, as they are optimized for performance and readability.
Avoid while and do-while loops unless necessary, as they can introduce errors and are generally less efficient than for loops.
Minimize Loop Overhead:
Cache loop lengths and constants outside the loop prevent recalculating them in each iteration. For example:

Reduce Nested Loops:
Nested loops can significantly slow down performance. If possible, flatten nested loops or use more efficient algorithms to handle complex iterations.
Avoid Modifying Loop Variables Inside the Loop:
Modifying loop counters or array elements inside a loop can lead to unexpected results and inefficient code execution. Keep loop logic straightforward and predictable.
Short-Circuit Conditions:
Use short-circuit evaluation to simplify and speed up conditional statements. For example, using && and || can prevent unnecessary evaluations:
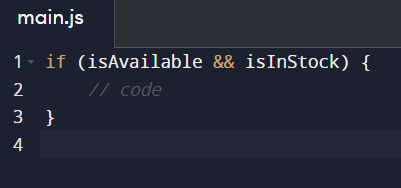
Optimize Conditional Statements:
Structure conditions to check the most likely true conditions first, minimizing the number of checks required. Also, avoid deeply nested conditionals when possible.
If you're looking to improve your web applications with optimized JavaScript, consider partnering with SayOne. At SayOne, we specialize in JavaScript development, offering expert solutions tailored to your specific needs.
With years of experience and a team of dedicated professionals, we ensure your web applications are fast and efficient. Page speed is crucial for user experience and search engine rankings, and our team is dedicated to implementing the best practices to enhance your site's performance.
Ready to optimize your web applications? Contact SayOne today!

We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.

About Author
Co-founder and CEO at SayOne Technologies | Helping startups and enterprises to set up and scale technology teams- Python, Spring Boot, React, Angular & Mobile.
We collaborate with visionary leaders on projects that focus on quality