
Subscribe to our Blog
We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.

Hari KrishnaNovember 5, 20219 min read

Generating table of contents...
Many organizations, large and small, are looking to shift to the microservices architecture model because it helps to easily scale up the scalability and maintainability of software applications in the organization. However, there may be challenges that you can encounter when you adopt the microservices model and how the AWS platform addresses these challenges. In an IBM survey, about 51% of the respondents complained of the lack of modern infrastructure required to effectively run microservices.
Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service) is a cloud computing service which is used to manage containers and to enable high scalability so that it becomes easy to run, stop and manage containers in a cluster.
Microservices are governed by a few fundamental concepts, such as:
Adopting microservices is, after all, not an easy job. Microservices are known to help organizations overcome limitations of the monolithic software applications that they use currently to run the organization, such as difficulty in scalability and less agility.
New users of microservices are likely to face challenges in the areas of latency, reliability, bandwidth, service discovery, versioning and cascading failures, among others.
Read our blog "How Kubernetes works to support microservices architecture".
As you know, the microservices architecture consists of a number of services. But then, how can you make sure that a specific service interacts with the latest upgraded version of another service? This is yet another challenge that you may face. However, a platform like Amazon ECS will help you to address these challenges and make your microservices adoption journey a smoother one.
As a fully managed container orchestration service, Amazon ECS is a reliable and cost-optimized service that can be coupled with other services from AWS, (like AWS Identity and Access Management, Amazon Routes 53, or Secrets Manager). Amazon ECS makes it easy for the user to deploy, scale and manage Docker containers that are used for running services, applications and batch processes. Additionally, these ECS services can be hosted on serverless infrastructure/virtual machines (Fargate/EC2 launch type, respectively).
The Amazon ECS computing platform works in the following manner. Basically, the components should be built up and further implemented to run in Docker containers. A Docker container is a standardized software development unit. Once the Docker containers are set up, the container images, a registry holds all the dock images from which appropriate images can be downloaded and run on Amazon ECS. To learn the structure of this service and to understand how it works, there are a few basic definitions that you have to know.
A Task is a text file (in JSON format) that describes a container (or more than one container). It is the most important part of Amazon ECS. The task definition is usually meant for a single container in the microservices architecture. Alternately, it can also be thought of as a microservice that includes many containers (for individual microservices).
Read our blog : Event Driven Microservices with Spring Boot
A task definition contains a number of settings such as a Docker image, an exposed port, the memory requirement, the command to run, cpu shares, and environmental variables.
A Task is a running container that has the settings defined already in the Task Definition. This can be thought of as an "instantiation" of a Task Definition. The Amazon ECS scheduler places the tasks in Amazon ECS and on the ECS Cluster.
This is a definition of long-running tasks of the same Task Definition. This may be just one running container or many of them using one Task Definition on a cluster. If one task fails, the service scheduler launches a new instance of the definition to replace the one that failed. Depending on the scheduling strategy that is chosen, the service maintains a specific number of tasks.
Download the ebook for FREE: "How to choose the best microservices vendor and trim the costs".
If you want to transition from legacy software into microservices architecture, speak to our expert developers today!
A logical grouping of resources on which the tasks run is called a cluster. For the Fargate launch-type, all the resources are managed by Amazon ECS. For EC2, the cluster is required to manage a bunch of container instances.
For the EC2 launch type, the container agent runs on each resource (infrastructure) within the ECS cluster. The container agent acts like a proxy between different tasks that reside on the EC2 resource and Amazon ECS. Its job is to start and stop tasks on request from Amazon ECS.
Amazon ECS-Elastic Container Registry
This is the AWS registry for Docker containers.
Application Load Balancer
The Application Load Balancer may be used to run the ECS service, and this helps to distribute the traffic across the tasks that are associated with the service.
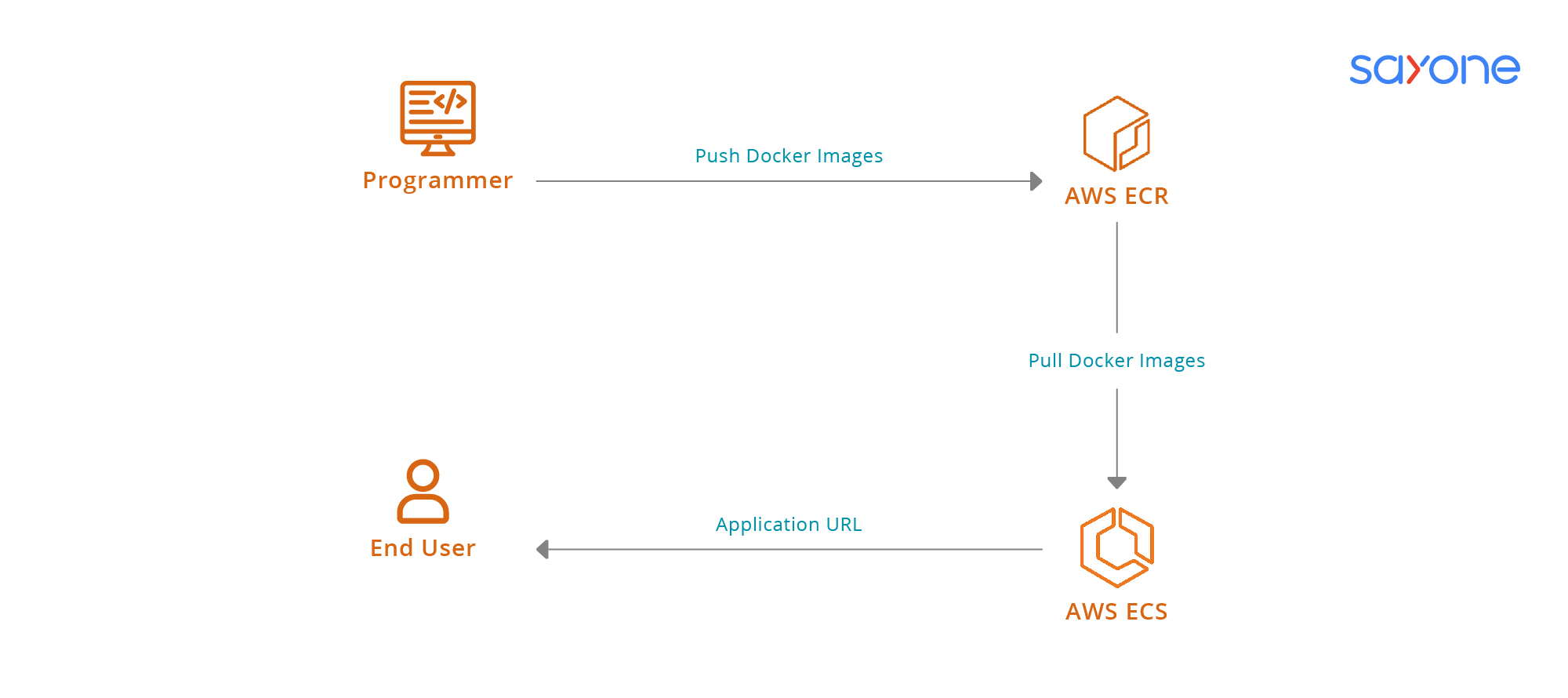
Microservices Architecture and Amazon ECS
Here, we give a brief example of how to design a workload for an online business. The solution has to scale according to the data load and be secure and reliable.
The first and foremost point to be deciphered is what the architecture of the current system looks like. Once the application is decoupled into individual domain-based services, the next step is to employ Amazon ECS.
Read our blog : What Kind of Challenges Can Microservices Help You Overcome
Assuming there are a few Docker containers making up the application that are prone to latency, we have to understand that it is a distributed system. Whenever there is a peak in one bandwidth or one of the microservices fails, Amazon ECS steps in to maintain the application's reliability and health.
Step 1: The application Load Balanced is put in the front and this works to distribute the traffic evenlu. The routing, however, has to be planned. The most common routing type chosen is path-based, that is, it routes the traffic to the microservice based on the API path received.
Step 2: The Application Load Balancer forwards traffic to the target Auto Scaling group (it is a group of EC2 resources that the container agents reside on). This will help to address bandwidth peaks that have occurred by suitably scaling up or down, as required.
Step 3: At this juncture, it is time to design the Amazon ECS service. First, a task definition is created using the URL of the Docker container. The service acts as the glue between the Load Balancer and task definition. Every service is associated with a target group.
Step 4: This architecture model solves cascade failures in two different ways. As the first step, Amazon ECS checks whether all the tasks are running; if not, a failed task is replaced with a new instance in order to meet the desired number of tasks within the service. Next, on the infrastructure level, health checks for target groups are conducted on the scheduled microservice path.
Step 5: When there is a new version of task definition that appears, its version is upgraded, all the currently running tasks are collapsed, and the deployment of new instances is according to the upgraded version. Another type of deployment by the ECS, other than the rolling update type, is the blue/green.
At SayOne, our integrated teams of developers service our clients with microservices that are future-ready for their organizations. The microservices we design and implement are formulated around the propositions of Agile and DevOps methodologies. Our system model focuses on individual components, all of which are resilient, robust, and highly reliable.
We design microservices for our clients that are fully adaptable in terms of scalability and adherence to the latest technologies. They are also constructed to accept fresh components easily and smoothly, allowing for effective function upgrades resulting in low workload costs.
Constructed with reusable components that offer increased flexibility, our microservices are designed to offer superior productivity for the organization/business. We work with businesses at different levels and help them to visualise the entire microservices journey prior to implementation and also allow for the effective coexistence of legacy systems of the organization.
Our microservices are developed for efficient performance, agility, and maintenance, scalability, enhanced performance, and security.
Final Thoughts
Amazon ACS is a handy tool that can help with quickly deploying, maintaining, and scaling a microservices architecture application. The ECS helps to overcome most of the challenges that are faced when setting up and running a microservices system.
Using Amazon ECS helps to lower workload costs, both CAPEX and OPEX. Additionally, employing ECS orchestration services also allows infrastructure flexibility.
Are you looking to reorganize your legacy software? Talk to us today!

We're committed to your privacy. SayOne uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. check out our privacy policy.

About Author
Helping Companies Scale Tech Teams 2X Faster with Pre-Vetted Talent | Contract Hiring & Resource Augmentation | Cutting Hiring Costs by 40%
We collaborate with visionary leaders on projects that focus on quality